News
5G: Connectivity and Driving Innovation

5G, the fifth generation of wireless technology, is not just an evolution but a revolution in connecting and interacting with the digital world. With significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than its predecessors, 5G is poised to transform industries, enhance everyday life, and drive innovation. This article delves into 5 G’s revolutionary potential, its benefits, applications, and challenges.
Understanding 5G Technology
Compared to 4G LTE, 5G technology is a significant advancement that offers previously unheard-of enhancements in several wireless communication areas. It provides the best performance by working in the low, mid, and high-frequency bands.
Key Features of 5G
- Speed: 5G can achieve download speeds of up to 10 Gbps, enabling near-instantaneous data transfer.
- Latency: 5G offers latency as low as one millisecond. It provides real-time responsiveness, which is crucial for autonomous vehicles and remote surgery applications.
- Capacity: 5G can support many devices per square kilometer, facilitating the Internet of Things (IoT) growth.
- Reliability: Enhanced reliability ensures consistent and stable connections, even in densely populated areas.
- Energy Efficiency: 5G networks aim to be more energy-efficient. Reducing power consumption for connected devices.
Spectrum Bands
5G utilizes a range of spectrum bands to deliver its capabilities:
- Low Band (Sub-1 GHz): Provides comprehensive coverage and penetration but lower speeds.
- Mid Band (1-6 GHz): Balances coverage and speed, suitable for urban and suburban areas.
- High Band (mmWave, 24-100 GHz): Offers ultra-fast speeds and low latency but limited coverage and penetration.

5G
Benefits of 5G
The advancements brought by 5G technology offer numerous benefits across various sectors, from healthcare and transportation to entertainment and manufacturing.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband
5 G’s quicker and more dependable internet connections make virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and high-definition video streaming possible. Users can use seamless connectivity and engaging content on their mobile devices.
Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion
5G is perfect for Internet of Things applications since it can link many devices simultaneously. 5G is needed to connect sensors, devices, and systems in smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation to increase productivity and quality of life.
Major Cities
5G makes monitoring and managing traffic, infrastructure, and public services in real-time in intelligent cities easier. This results in better urban design, lower energy use, and more public safety.
Industrial interest in 5G
5G enables effective supply chain management, predictive maintenance, and automation in manufacturing and logistics. The seamless operation and communication of connected equipment and devices can increase productivity and decrease downtime.
Critical Communications of 5G
5G’s high dependability and low latency are essential for applications that need accuracy and real-time communication. This covers emergency response systems, remote surgery, and driverless cars.
Driverless Automobiles
5G improves safety and permits autonomous driving by allowing real-time communication between automobiles and infrastructure. This could lower traffic accidents, enhance traffic flow, and open the door for entirely driverless vehicles.
Remote Medical Care
5G enables robotic surgery, remote monitoring, and telemedicine in the healthcare industry. Remote medical procedures and consultations would allow doctors to provide better access to care, particularly in underserved and rural locations.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promising potential, 5G faces several challenges and considerations that urgently need to be addressed for widespread adoption and success. It’s crucial that we tackle these challenges head-on to fully realize the benefits of 5G.
Infrastructure and Deployment
Installing 5G infrastructure will cost a lot of money and time. Despite having faster speeds, the high-frequency mmWave bands have a narrow penetration and range, requiring a dense network of tiny cells and antennas. This requires significant preparation, expense, and coordination with local authorities.
Privacy and Security
As 5 G connects more systems and devices, there is a greater chance of cyberattacks and data breaches. It is essential to guarantee robust security protocols and safeguard user privacy. This entails enforcing strict authentication procedures, encrypting data, and protecting the network infrastructure.
Spectrum Allocation and Regulation
5G spectrum management and allocation present regulatory concerns. To prevent interference and guarantee peak performance, governments and regulatory agencies must work together to coordinate and distribute spectrum effectively. International collaboration to standardize spectrum usage is part of this.
Summary
5G technology, with its unmatched speed, low latency, and extensive connectivity, is a revolutionary step forward in wireless communication. It has the potential to significantly improve daily living, from healthcare and transportation to entertainment and manufacturing. Despite the obstacles in the form of regulations, security, and infrastructure deployment, the advantages of 5G are expected to propel major developments and influence the direction of connectivity in the future. A more connected and smarter society is on the horizon as 5G rolls out internationally and opens up new opportunities.
News
Diddy News: Exploring the Latest
News
The Pizza Edition: Explore the Best Variations of Pizza
News
der elefantenbulle ahmed: Legend of the Last Great Tusker
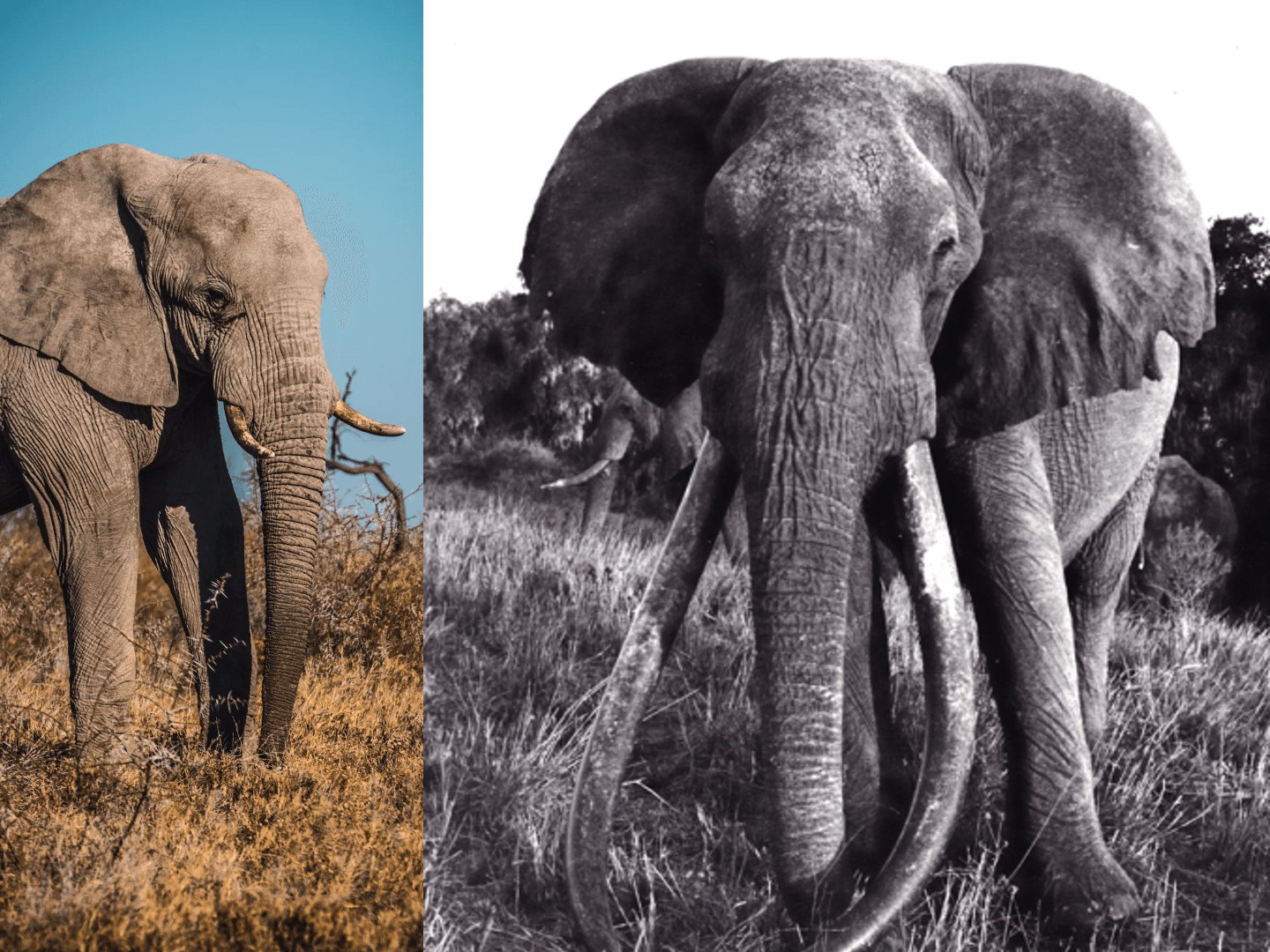

Der Elefantenbulle Ahmed
Der Elefantenbulle Ahmed is one of the most well-known and iconic figures in Kenya’s wildlife history. A magnificent African elephant (Loxodonta africana), Ahmed became famous for his exceptionally long tusks and his role as a symbol of conservation in Africa. In this article, we will explore Ahmed’s story, his significance and his legacy.
The story of Der Elefantenbulle Ahmed
Der Elefantenbulle Ahmed, lived in the Marsabit National Reserve in northern Kenya in the 1960s and 1970s. He was known for his impressive size and exceptionally long tusks, which made him one of the last so-called “Great Tuskers.” A “Great Tusker” is an elephant whose tusks weigh over 100 pounds (about 45 kilograms) each. Ahmed’s tusks were not only exceptionally long, but also very heavy, making him a special attraction and a valuable target for poachers.
Ahmed as a symbol of nature conservation
At a time when poachers posed a significant threat to the elephant population in Africa, Ahmed became a symbol for the protection of endangered species. His unique appearance and gentle nature attracted the attention of conservationists and the public. The Kenyan government recognized Ahmed’s importance to conservation and took unprecedented measures to protect his life.
In 1970, then President of Kenya, Jomo Kenyatta, officially declared Ahmed a “living monument.” This declaration was a first in Kenya’s history and highlighted the bull elephant’s importance to the nation and to conservation worldwide. As a result of this declaration, Ahmed was given 24-hour protection by armed guards. These protective measures were crucial to protect him from poachers who were after his valuable tusks.
The last years and the death of Ahmed
Ahmed lived to a ripe old age, dying of natural causes in 1974 at the age of about 55. His death was a significant event that received worldwide attention. The fact that his body was found intact shows that the Kenyan government’s conservation efforts were successful and Ahmed was protected from poachers throughout his life.
After his death, Ahmed’s body was dissected and put on display at the Nairobi National Museum. This exhibition is intended to honour his life and legacy and serve as a reminder of the importance of conservation and the need to protect endangered species.
Der Elefantenbulle Ahmed legacy and its significance today
Ahmed the bull elephant remains a symbol of conservation in Africa today. His story has inspired generations of conservationists and raised awareness of the need to protect endangered species. He represents the urgent need to protect wildlife from the threats posed by human activities such as poaching and habitat loss.
Ahmed’s legacy also lives on in ongoing efforts by Kenya and other countries to protect and conserve elephant populations. Thanks to modern technology and dedicated conservation organizations, many elephants are now better protected through strict laws and monitoring programs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why did the bull elephant Ahmed become famous?
- Ahmed became famous for his exceptionally long tusks and his status as one of the last “Great Tuskers” in Africa. He also became a symbol of conservation because he was given special protection by the Kenyan government.
2. What does it mean that Ahmed was a “living monument”?
- A “living monument” is an official designation given to Ahmed by the then President of Kenya, Jomo Kenyatta. This designation meant that Ahmed was placed under permanent protection to protect him from poachers.
3. How was Ahmed’s body treated after his death?
- After his death, Ahmed’s body was dissected and exhibited at the Nairobi National Museum to honor his legacy and highlight the importance of conservation.
4. What does Ahmed’s story mean for modern conservation?
- Ahmed’s story highlights the importance of protecting endangered species and continues to inspire conservation efforts around the world. It shows that individual actions to protect individual animals can have a significant impact on the protection of entire species.
Conclusion
The bull elephant Ahmed is more than just a historical figure; he is a symbol of the importance of conservation and the fight against poaching in Africa. His story reminds us of the importance of protecting our natural resources and preserving biodiversity. Ahmed’s legacy lives on and inspires us to continue fighting to protect elephants and other endangered species.
-

 News5 months ago
News5 months agoBrooke Tilli – Bio, Age, Relationships, Career, Net Worth, and Boyfriend
-

 Celebrity4 months ago
Celebrity4 months agoPedro Vaz Paulo: A Life of Redemption
-

 Celebrity4 months ago
Celebrity4 months agoBurak Deniz: The Turkish Heart-Throb
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoCloud Computing: Enabling IT Innovation
-

 News5 months ago
News5 months agoDefine a Offshore Accident Lawyer
-
 Tech4 months ago
Tech4 months agoSaaS Integration: Cloud-Based Software
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoJanitor AI: Future of Auto Maintenance
-

 News5 months ago
News5 months agoAI Deepfake Threaten to Global Elections. No One Can Stop Them.





